Setting Up a Remote Podman Service
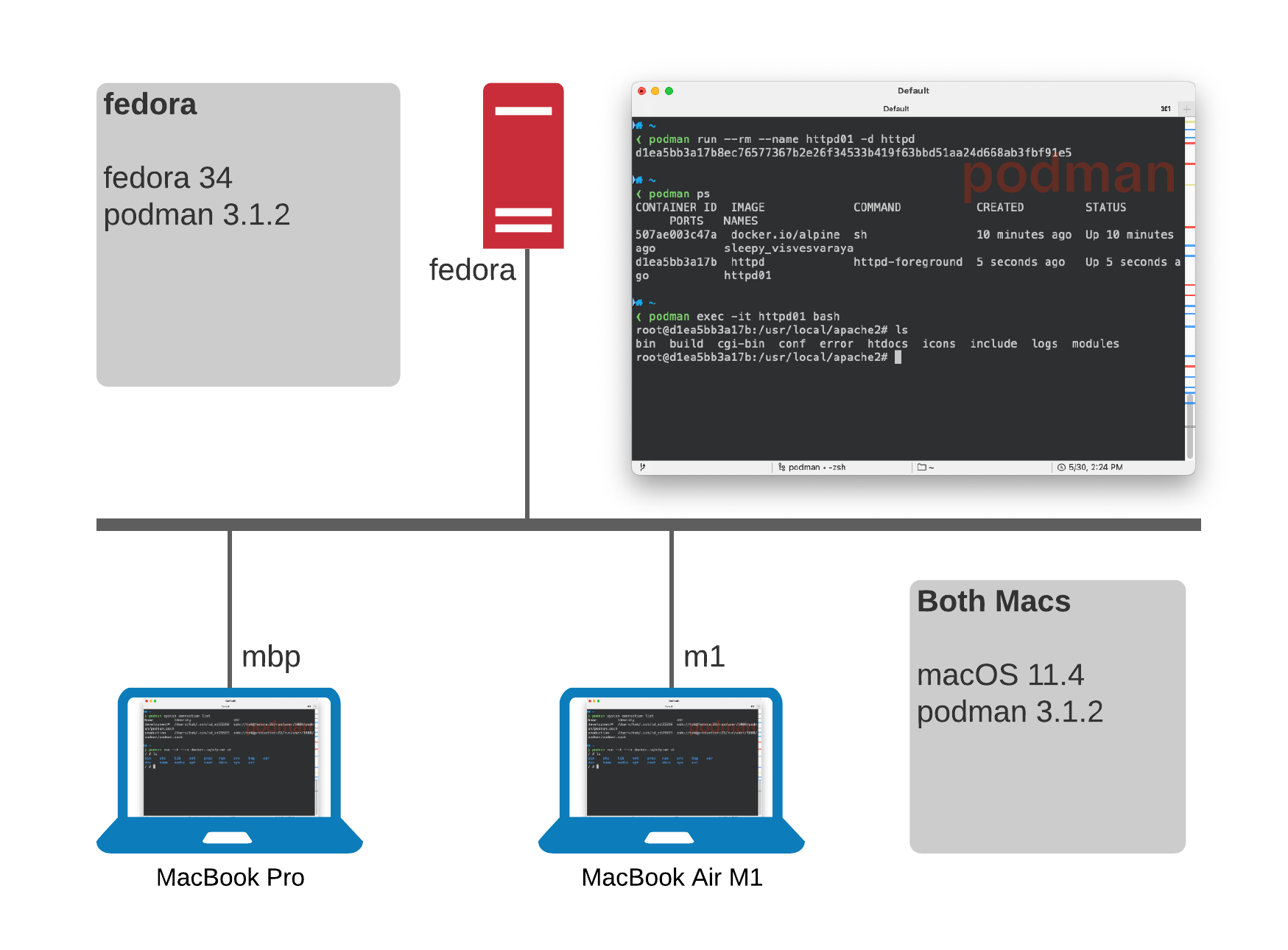
Overview
Setup up a Linux instance to act as a podman server allowing you to run podman and podman-compose commands remotely.
So for example you can develop on a Mac, but run containers via podman and podman-compose at least some of the time.
This article will show you how to:
-
Setup a remote
podmanserver (RHEL, Fedora, CentOS - Ubuntu should just be package changes) -
Setup podman remote client on your Mac (Should work for Windows and Linux too)
Background
For an increasing number of reasons lately I’ve been defaulting to podman more and more on my Mac though I still also have docker installed and use both day to day.
I’m not going to go into the pros and cons of both in this article but there are some resources at the end of this article.
Setting up podman remote client has been covered before, for example Podman remote clients for macOS and Windows and in the repo’s Podman remote-client tutorial itself however I found a couple of gotchas hence this article. The goal is for this to be a comprehensive HOWTO. which should work if followed on both x86 and M1 Macs.
Pre-Requisites
-
Linux host e.g. a home-lab machine or Linux VM
-
Pretty much any Mac, M1 or x86 (the instructions below should work with few changes for Windows or another Linux client if you have a use case)
Part 1: Setting up your Podman Host
So recently I built a powerful home-lab machine to run Fedora and planned to use it to learn KVM better and run VMs.
In my case, and this is way overkill for typical needs, I built an 8 core AMD Ryzen 3800 based system with a generous with 128GB RAM, and a 1GB M2 drive.
Currently it runs Fedora 34 and Podman 3.1.2.
This article should work fine with far more modest configurations.
-
Install podman
-
Enable podman daemon to listen for remote request
-
setup ssh keys - careful here, it’s a little fussy
-
Add the remote podman service to the Mac
Install and Enable podman
Assumptions: You already have a running fedora (RHEL, CentOS, etc should work fine), with sshd already configured.
-
Install
podmanand the optional compose componentsfedora $ sudo dnf install -y podman docker-compose podman-compose -
Enable and start the service for your user by enabling the
podman.socketfedora $ systemctl --user --now enable podman.socket -
Keep the socket alive with
lingerwill ensure thepodmanservice is always available irrespective of whether you are logged in or notfedora $ sudo loginctl enable-linger $USER
Verify the podman.socket is listening
There are a number of ways we can confirm the socket is now listening.
-
Easiest is to query with
systemctlfedora $ systemctl status podman.socket● podman.socket - Podman API Socket Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/podman.socket; enabled; vendor preset: disabled) Active: active (listening) since Sat 2021-05-29 07:01:11 EDT; 1 day 3h ago Triggers: ● podman.service Docs: man:podman-system-service(1) Listen: /run/podman/podman.sock (Stream) CGroup: /system.slice/podman.socket -
You can also simply
curlthepodman.socketfedora $ curl --unix-socket /run/user/1000/podman/podman.sock http://localhost/_pingOK%NoteThe path above contains your User ID /run/user/<USER_ID>/…which you can obtain withidRemember this as you’ll need during the setup section on your Mac.
Setup ssh authentication on your Mac
This was the part that initially caught me out.
I’d been using RSA keys for years so I initially tried it with my id_rsa key.
This was also how I had seen examples both in the docs and in at least one blog article.
Turns out at some point, I’m assuming relatively recently, support for RSA keys has either been dropped in favor of the more recent, and secure, ed25519 keys or I simply caught a bug/issue.
Certainly there were other users caught by this.
|
Note
|
Reading through closed Issues in the Podman Repo it may be that RSA keys do now again work. Testing this is an exercise for the reader, and hey ed25519 keys are stronger! |
|
Important
|
This section is performed on your Mac. (should also work on a Windows/Linux host) |
-
Generate your ed25519 key if you don’t already have one
mac $ ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -C "jdoe@example.com" -
Copy your new key from your Mac to your podman host, in my case
fedoramac $ ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_ed25519 fedora -
Validate by ssh’ing to your podman machine explicitly using the new key
mac $ ssh tok@fedora -i ~/.ssh/id_ed25519Last login: Sun May 30 09:40:05 2021 from 192.168.1.54 fedora $
Part 2: Connect to the podman Service
Setting up your Mac. I’m a sort of latest and greatest person so today this is running on the latest Big Sur 11.4 and I mix an older MBP 16” with a new MacBook Air M1 which is an awesome portable rocket ship. Despite using Ansible for most things lets keep this simple:
-
Install podman on your Mac
mac $ brew install podmanNoteI’m assuming your
PATHis setup correctly/usr/local/binon x86 and/opt/homebrew/binon the M1. Incidentally it’s worth noting if you are installing on an M1 based system that it is actually an ARM based package:Pouring podman—3.1.2.arm64_big_sur.bottle.tar.gz -
Add the remote
podmanservicemac $ podman system connection add development --identity ~/.ssh/id_ed25519 ssh://homelab/run/user/1000/podman/podman.sockNote-
The
developmentin the above command should be a meaningful name for your remote system as you can have multiple remote podman services -
Remember you need your remote User ID which if you’ve forgotten can easily be retrieved eg:
ssh tok@fedora -i ~/.ssh/id_ed25519 iduid=1000(tok) gid=1000(tok) groups=1000(tok),36(kvm) context=unconfined_u:unconfined_r:unconfined_t:s0-s0:c0.c1023
-
Test your system
Now you should be able to access and use podman from your Mac
-
List the podman system connection services
mac $ podman system connection listName Identity URI development* /Users/tok/.ssh/id_ed25519 ssh://tok@fedora:22/run/user/1000/podman/podman.sock production /Users/tok/.ssh/id_ed25519 ssh://tok@production:22/run/user/1000/podman/podman.sockTipHere there are 2 remote systems which can both be used, including our new
developmentservice we just created. To set the default, heredevelopment, on your Mac:podman system connection default development -
Now test from your Mac
mac $ podman system info | headhost: arch: amd64 buildahVersion: 1.20.1 cgroupManager: systemd cgroupVersion: v2 conmon: package: conmon-2.0.27-2.fc34.x86_64 path: /usr/bin/conmon version: 'conmon version 2.0.27, commit: ' cpus: 16 -
Launch your first image, let’s use
alpinesince it’s nice and smallmac $ podman run -it --rm docker.io/alpine shTrying to pull docker.io/library/alpine:latest... Getting image source signatures Copying blob sha256:540db60ca9383eac9e418f78490994d0af424aab7bf6d0e47ac8ed4e2e9bcbba Copying config sha256:6dbb9cc54074106d46d4ccb330f2a40a682d49dda5f4844962b7dce9fe44aaec Writing manifest to image destination Storing signatures / # uname -a Linux 21bd9e863f71 5.12.7-300.fc34.x86_64 #1 SMP Wed May 26 12:58:58 UTC 2021 x86_64 Linux -
In another terminal on your Mac check what’s running
mac $ podman psCONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 21bd9e863f71 docker.io/library/alpine:latest sh 4 minutes ago Up 4 minutes ago beautiful_ishizaka -
And also from your Linux host try the same
podman psfedora $ podman psCONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 21bd9e863f71 docker.io/library/alpine:latest sh 4 minutes ago Up 4 minutes ago beautiful_ishizakaNotepodman and docker typically default to different registries so for example
docker run -d httpdwill default todocker.io/httpdwhilstpodmanwill not. So make sure to qualify your image names or you may see unexpected results.
Cheatsheet
| List | Command |
|---|---|
podman system info |
|
Add podman remote system |
|
Remove podman remote system |
|
List podman systems |
|
Make podman system |
|
Conclusion
So now you can seamlessly run containers using podman on one, or more, remote systems.
This HOWTO can easily be extended to allow access to a similar remote service running as root if necessary. <INSERT usual security warnings!!>
In future articles I want to explore topics including:
-
Creating podman based
systemdservices -
Running your own long lived registry
-
docker-composeandpodman-compose
Resources
-
Alternative, and earlier article, on Setting up a Remote Podman Service
